AI as Architect: How Intelligent Systems Accelerate and Scale Immersive Tech Solutions

The production timeline for a high-fidelity immersive experience used to stretch across months. Designers would painstakingly model every texture, adjust every light source, and manually iterate through design variations until something clicked. That world still exists, but it's rapidly becoming a relic.
Today, intelligent systems are fundamentally reshaping how immersive environments come to life—not through shortcuts or compromises, but through architectural thinking at scale. What we're witnessing isn't just faster production. It's a complete reimagining of how virtual spaces, interactive installations, and sensory-rich environments are conceived, developed, and deployed across enterprise applications.
For marketing leaders, innovation heads, and C-suite executives evaluating immersive technology investments, understanding this shift isn't optional anymore. The competitive advantage now belongs to organizations that can deliver complex virtual experiences without sacrificing quality, personalization, or operational efficiency.
The Foundation: Intelligent Systems as Design Partners
Think of intelligent systems less as tools and more as collaborators in the design process. They don't replace creative vision—they amplify it by handling the computational heavy lifting that traditionally consumed entire production cycles.
Automated Content Generation That Actually Works
The promise of automated 3D asset creation has been around for years, but recent advances in generative models have finally delivered on that promise. What changed? The systems learned to understand context, aesthetic principles, and technical constraints simultaneously.
Faster asset development means teams can generate detailed 3D models, realistic textures, and complete landscape environments from text descriptions or reference parameters. Projects that once required dedicated modelers for weeks now see first drafts within hours. But speed alone misses the point—the real value lies in exploration velocity.
Architects and experience designers can now test dozens of spatial configurations, material choices, and lighting scenarios in the time it previously took to finalize a single option. This isn't about cutting corners; it's about expanding the creative possibility space before committing resources to final production.
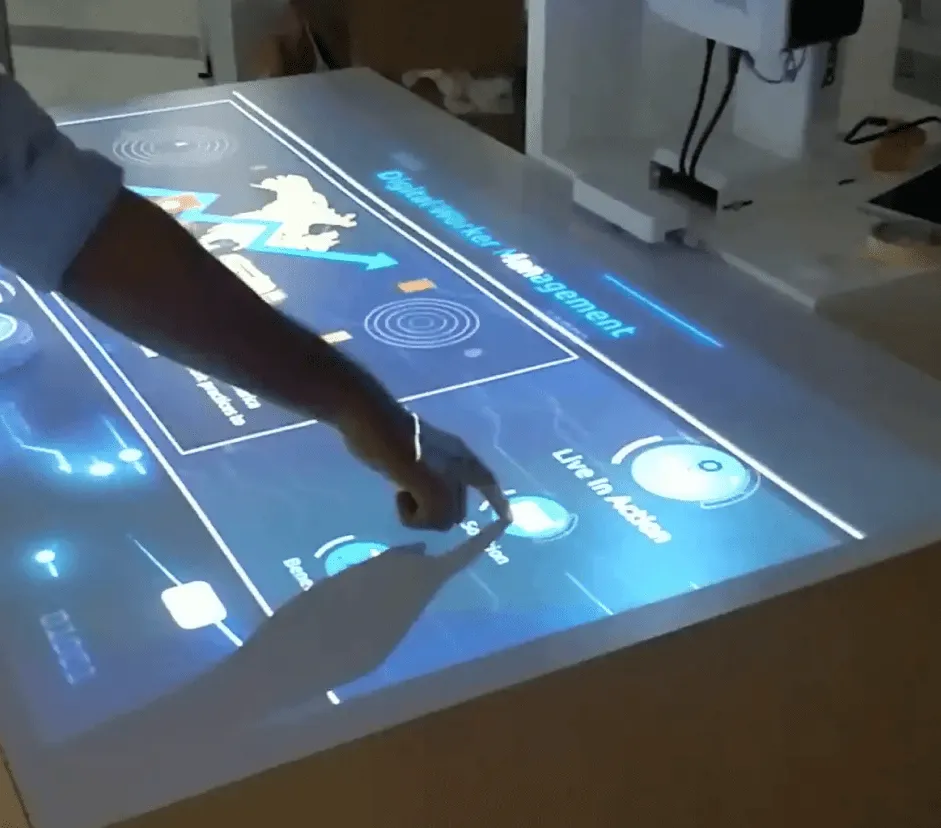
Rapid prototyping transforms how teams approach feasibility studies. When you're planning an Experience Centre for a retail flagship or mapping out a virtual product launch environment, the ability to visualize multiple approaches quickly changes the conversation. Stakeholders see options, not proposals. Decisions happen based on comparative analysis rather than theoretical descriptions.
Dynamic content generation introduces another dimension entirely. Instead of static environments that look identical for every visitor, intelligent systems enable spaces that respond and evolve. A virtual showroom can reconfigure itself based on visitor behavior. Training simulations adjust difficulty and scenarios on the fly. Brand activations shift their narrative emphasis depending on real-time engagement patterns.
Realism That Closes the Believability Gap
Immersive technology succeeds or fails on one metric that's difficult to quantify but impossible to ignore: believability. Visitors to an Experience Centre or participants in a VR training module make split-second judgments about whether what they're seeing feels real enough to engage with seriously.
Intelligent systems contribute here through advanced rendering techniques that would be computationally prohibitive to calculate manually. Neural networks analyze how light behaves in physical spaces and apply those principles to virtual objects in real-time. The result? Digital products placed in augmented reality don't just appear in your space—they cast accurate shadows, reflect ambient light conditions, and integrate seamlessly with their surroundings.
Physics simulations powered by machine learning create environments where objects behave as they would in reality. This matters enormously for training applications in manufacturing, healthcare, or logistics, where muscle memory and spatial understanding directly translate to real-world performance. A surgeon practicing a procedure in VR needs instruments that respond with realistic resistance and movement. Industrial workers training on safety protocols need equipment that reacts to mishandling the way actual machinery would.
Performance optimization happens automatically across different hardware configurations. The same immersive content that runs flawlessly on high-end VR headsets can be intelligently scaled for deployment on tablets or smartphones without manual reengineering. Systems analyze the available processing power and adjust rendering quality, physics calculations, and interactive elements accordingly.
Project Management That Scales With Complexity
Large-scale immersive projects involve coordinating multiple disciplines: 3D artists, developers, content strategists, hardware specialists, and often client stakeholders across different time zones. Intelligent systems streamline this coordination through predictive project management capabilities.
Resource optimization algorithms analyze project requirements and automatically suggest task sequencing, identify potential bottlenecks, and flag resource conflicts before they impact timelines. When you're building a multi-room Experience Centre with synchronized content across projection mapping, interactive displays, and spatial audio, keeping everything aligned is non-trivial. Intelligent project management tools make it manageable.
Automated documentation handles the tedious but essential work of tracking changes, maintaining version control, and generating compliance reports. For projects involving architectural visualization or installations in regulated spaces, automated clash detection in Building Information Modeling systems catches conflicts that human review might miss.
Data-driven decision support provides project leads with scenario analysis. What happens to the timeline if material delivery delays by two weeks? How does choosing a different rendering approach affect both quality and completion date? These aren't hypothetical questions—they're the daily reality of complex projects, and having quantitative answers changes how confidently teams can commit to deliverables.
Scaling Solutions: From Prototype to Platform
Creating one impressive immersive experience is a creative achievement. Creating fifty customized versions that maintain quality while serving different audiences, locations, and objectives? That's an operational challenge that intelligent systems are uniquely positioned to solve.
Personalization Without Manual Customization
Generic experiences don't drive results. A retail executive touring a virtual flagship store needs different information highlighted than a franchise owner evaluating the same space. A new employee in VR onboarding requires different pacing than someone with industry experience.
Intelligent systems enable adaptive content delivery by continuously analyzing user interactions and adjusting what's presented accordingly. In a property technology application, virtual tours can emphasize architectural features for design-focused visitors while surfacing investment metrics for financial decision-makers—all without creating separate experiences.
Voice-activated navigation through Natural Language Processing eliminates the learning curve that typically accompanies new interface paradigms. Visitors to an Experience Centre can simply ask questions and receive contextual responses, making the technology feel intuitive rather than impressive-but-intimidating.
Progressive learning systems track competency development in training applications, automatically adjusting scenario complexity to maintain optimal challenge levels. This ensures that immersive training programs remain effective across skill ranges without requiring manual curriculum management for every participant.
Cross-Platform Deployment That Expands Reach
Hardware limitations have historically constrained immersive technology adoption. High-quality experiences demanded high-end equipment, limiting deployment to controlled environments or early adopters willing to invest in premium devices.
Cloud-based rendering architectures change this equation by processing intensive graphics remotely and streaming the results to user devices. Suddenly, a smartphone can deliver experiences that would normally require dedicated VR hardware. For brands planning widespread activations across retail locations or event venues, this accessibility transformation is game-changing.
Edge computing infrastructure brings processing power physically closer to where experiences happen, reducing latency to imperceptible levels. This matters critically for interactive installations where any delay between user action and system response breaks immersion. As immersive deployments scale across multiple locations, edge architecture ensures consistent performance regardless of network variability.
Analytics That Drive Continuous Improvement
Intelligent systems don't just enable immersive experiences—they make those experiences measurable in ways that inform strategic decisions.
Behavioral analysis tracks how people actually interact with immersive content. Where do visitors spend the most time? Which features generate engagement versus confusion? What sequence of interactions correlates with desired outcomes? These insights emerge from analyzing thousands of individual sessions, identifying patterns that would be invisible in small sample sizes.
Predictive modeling applies historical interaction data to forecast future behavior and preferences. For retail applications, this means anticipating which product categories warrant expanded virtual presence. For training programs, it identifies which scenario types produce the strongest skill retention. For brand activations, it reveals which narrative approaches resonate most strongly with target audiences.
Real-World Applications Across Industries
The architectural role of intelligent systems manifests differently depending on industry context, but the underlying principles remain consistent: accelerate production, personalize at scale, adapt in real-time.
Property technology and real estate leverage intelligent systems for virtual property tours that go far beyond passive walkthroughs. Prospective buyers receive personalized insights about features matching their stated preferences. Comparative market analysis appears contextually when viewing specific properties. Financing options adjust in real-time based on expressed interest. These capabilities transform property marketing from information delivery into consultative engagement.
Urban planning and architectural firms use intelligent design tools for rapid site analysis and generative design exploration. When evaluating potential development sites, systems can instantly model environmental factors, solar exposure, wind patterns, and pedestrian flow. Generative algorithms produce multiple design variations optimized for different priorities—sustainability, cost efficiency, spatial capacity—allowing stakeholders to make informed tradeoffs rather than accepting single proposals.
Enterprise training and simulation deploy hyper-realistic scenarios for high-stakes skill development. Medical professionals practice complex procedures. Industrial workers train on equipment operation and safety protocols. Autonomous vehicle algorithms test edge cases. The ability to create unlimited scenario variations without physical risk or resource consumption makes immersive training economically viable at scale.
Retail and consumer brands implement augmented reality applications that let customers visualize products in their actual spaces before purchase. Virtual try-ons for apparel and cosmetics reduce return rates. Furniture placement tools increase purchase confidence. These applications succeed when they feel helpful rather than gimmicky—a balance that intelligent personalization systems help maintain.
The Production Reality: What Actually Changes
For teams building immersive experiences professionally, intelligent systems shift where time gets invested rather than eliminating work entirely.
Manual modeling of every asset becomes selective rather than universal. Teams focus creative energy on hero elements while intelligent systems handle background detail and variation generation. Quality control shifts from pixel-level perfection to ensuring system outputs align with creative direction.
Iteration cycles compress dramatically. What used to require full production passes now happens through parameter adjustments and automated regeneration. This doesn't make design easier—it makes it more demanding because the barriers to exploring alternatives disappear. Teams must develop stronger initial concepts because they'll have time to test many of them.
Collaboration becomes less about file transfers and version reconciliation, more about shared access to living projects where changes propagate automatically. Remote teams work together with friction that previously required everyone in the same physical space.
Emerging Frontiers: Multi-Sensory Integration
The next evolution of immersive experiences extends beyond visual and auditory engagement into full sensory orchestration. Intelligent systems coordinate haptic feedback, spatial audio, even scent and temperature variations to create comprehensive environmental narratives.
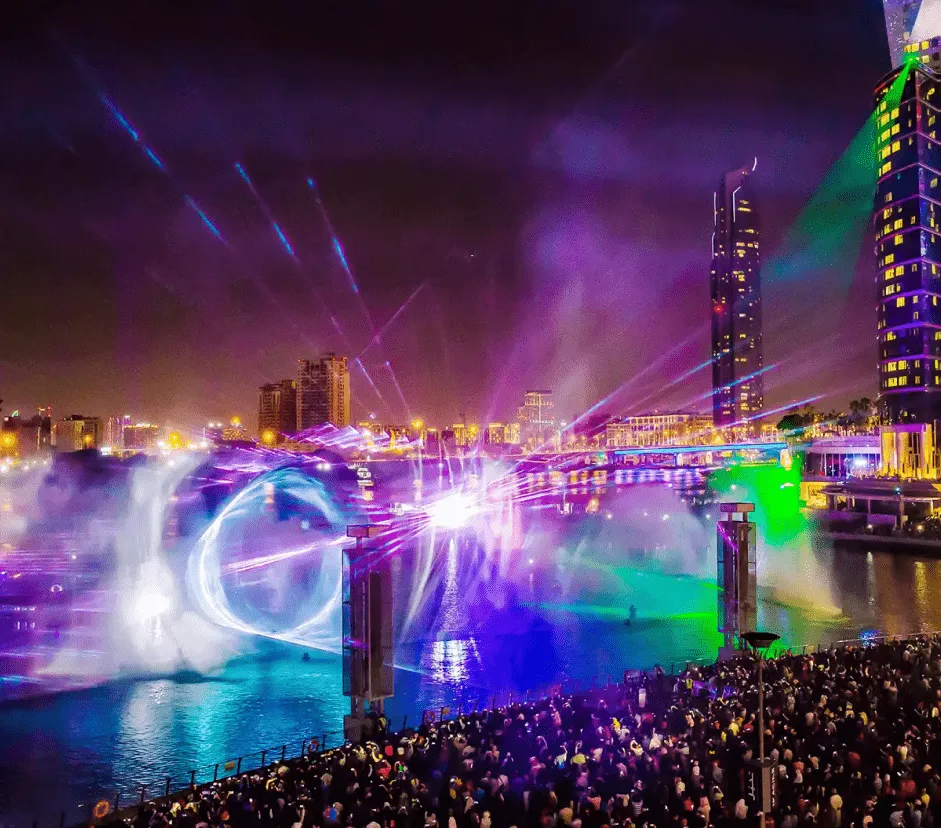
Experience Centres increasingly deploy these multi-sensory approaches for brand storytelling that creates lasting memory formation. When visitors don't just see and hear a brand story but physically feel relevant elements, the neurological impact differs fundamentally from traditional marketing touchpoints.
Internet of Senses integration allows immersive environments to connect with smart building systems, wearable devices, and environmental sensors. An installation might adjust its narrative pacing based on crowd density, modify visual complexity when it detects visitor fatigue, or heighten dramatic elements when biometric feedback indicates high engagement.
These capabilities aren't science fiction—they're active deployments in premium brand activations and flagship Experience Centres. The intelligence layer coordinating these elements ensures they enhance rather than overwhelm, adapting to individual and collective response patterns.
Strategic Considerations for Implementation
Organizations evaluating intelligent systems for immersive technology must address several non-technical factors that determine success.
Data governance frameworks need establishment before deployment, particularly for applications that personalize based on user behavior. Clear policies about what gets collected, how it's used, and how long it's retained aren't just regulatory compliance—they're essential for maintaining user trust.
Accessibility standards should be architectural from the beginning, not retrofitted later. Intelligent systems can help by automatically generating alternative interaction modes, but only if accessibility is defined as a core requirement rather than an accommodation.
Ethical content generation protocols matter when systems create experiences autonomously. What boundaries constrain the variations that generative systems can produce? Who reviews outputs before they reach audiences? These governance questions demand answers before production scales.
Making the Shift
For marketing leaders, innovation directors, and C-suite executives, the strategic question isn't whether intelligent systems will transform immersive technology production—that's already happening. The question is whether your organization will lead that transformation or respond to it.
The competitive dynamics are shifting quickly. Brands that master intelligent system integration can deliver more sophisticated immersive experiences, faster and at greater scale than competitors working with traditional production methods. The quality gap is closing while the efficiency gap widens.
Start with pilot projects that test capabilities without betting the entire innovation budget. Build internal literacy about what these systems actually do versus what marketing materials claim. Develop partnerships with production teams that demonstrate practical expertise rather than just technical credentials.
The most successful implementations we've seen combine strong creative vision with technical pragmatism. The intelligence handles computational complexity; your team provides the strategic and aesthetic judgment that makes experiences meaningful rather than merely impressive.
Immersive technology powered by intelligent systems isn't a future trend—it's the current reality for organizations serious about experiential engagement. The question worth asking yourself: what becomes possible for your brand when production constraints stop limiting your creative ambition?
If you're ready to explore what intelligent immersive solutions could mean for your next launch, activation, or Experience Centre, the conversation starts with understanding what you're trying to achieve, not what the technology can theoretically do. That's where practical innovation begins.
Contact Us Now:





.CNhas5IL_ZqBJiz.webp)